| 摘要 | 包装容器的阻氧性能测试是包装检测行业内的一大难题,现在已取得了一定的进展 。兰光推出的 TOY-C1容器/薄膜透氧仪, 满足ASTM F1307.ASTM D3985等国际高标准要求,检测包装物的氧气透过率。 |
|---|---|
| 关键字 | 包装容器,阻氧性能,容器薄膜透氧仪 |
| 文档 | 点击查看PDF文档 |
随着包装行业发展的日新月异,轻巧且方便运输的包装容器,如 PET塑料瓶、纸塑铝复合软包装等新型材料逐步取代了笨重、易碎的玻璃瓶包装,然而这些新型包装材料的性能,尤其是阻隔性能能否满足产品包装的质量要求呢?这是消费者、包装产品的使用者及制造者、各级质检机构共同关心的话题,同时也是急需解决的问题。目前国内尚没有明确的包装物透氧性测试方法标准,因此在进行相关测试时一般遵循ASTM F 1307标准。
本文结合 ASTM F 1307标准,对有关包装容器的透氧性测试给以简单介绍。
1、适用范围
This test method covers a procedure for the determination of the steady-state rate of transmission of oxygen gas into packages. More specifically, the method is applicable to packages that in normal use will enclose a dry environment. ( 这个测试方法探讨了一种用于确定氧气渗透进入包装物的稳定渗透速率的测试方法。更明确地说,这种测试方法适用于在通常使用时能够封起一个干燥空间的所有包装物。 )
2、测试方法概要
This test method employs a coulometric oxygen sensor and associated equipment in an arrangement similar to that described in Test Method D 3985. Oxygen gas transmission rate ( O2 GTR ) is determined after the package has been mounted on a test fixture and has equilibrated in the test environment. The package is mounted in such a way as to provide that the inside of the package is slowly purged by a stream of nitrogen while the outside of the package is exposed to a known concentration of oxygen. The package may be exposed in ambient room air which contains 20.8% oxygen, or immersed in an atmosphere of 100% oxygen. As oxygen permeates through the package walls into the nitrogen carrier gas, it is transported to the coulometric detector where it produces an electrical current, the magnitude of which is proportional to the amount of oxygen flowing into the detector per unit of time.(这种试验方法按照与测试方法D 3985 所描述的相似方式使用库仑氧气传感器及其相关设备。氧气透过率(O2 GTR)是将包装物固定在测试装置上并在测试环境中达到平衡后测定的。包装物装夹完成后能够形成如下的测试环境:包装物内侧被氮气流缓慢净化、外侧暴露在氧气浓度已知的环境中。包装物可以暴露在环境大气中,它含有20.8%的氧气,或者是浸在100%的氧气环境中。当氧气渗透通过包装物壁进入载气氮气流中,它会被载气流携带至库仑传感器处,库仑传感器探测到氧气会输出电流,电流的大小与单位时间内流入传感器的氧气总量成正比。)
这种试验方法中采用氧气作为测试气体,氮气作为载气气体。在包装物的外部和内部形成一定的氧浓度差,外部为氧浓度高的一侧,而内部为氧浓度低的一侧,在整个渗透过程中氧气从包装物外部透过包装物壁向内部渗透。
3、包装物透氧性测试数据的表示方法
Oxygen gas transmission rate ( O2 GTR )——as applied to a package, is the quantity of oxygen gas passing through the surface of the package per unit of time… The SI unit of transmission rate is the mol/pkg·s. The test conditions, including temperature, oxygen partial pressure and humidity on both sides of the package, must be stated. A commonly used unit of O2 GTR is the cm3( STP )/pkg·d, where 1 cm3 ( STP ) is 44.62×10 -6 mol.(包装物的氧气透过率是单位时间内渗透通过包装物表面的氧气总量。……它的SI单位是mol/pkg·s。必须写明测试状态,包括温度、氧气分压差、以及包装物两侧的湿度。O2 GTR的常用单位是cm3( STP )/pkg·d,这里1cm3 ( STP ) 等于 44.62×10 -6 mol。)Oxygen permeance ( PO2 ' )——the ratio of the O2 GTR to the difference between the partial pressure of O2 on the two sides of the package wall.(氧气渗透量是O2 GTR 与包装物壁两侧氧气分压差的比值。)由于在一定的环境条件下,透过的氧气摩尔数与它的体积可互相转换,因此无论是用摩尔数表示还是使用气体体积表示,含义都是相同的。
如果将包装物的测试结果单位与薄膜的测试结果单位相比较不难发现,测试面积没有了,这表示它不再参与计算,取而代之的是一个 pkg单位。
3.1 pkg 的定义
对于没有接触过包装物阻隔性测试的人来讲,会感到这个单位非常陌生,其实它就是一个适用于任何包装物的数量单位,相当于件、包,是package的简写。例如,2.25L的PET瓶或是1L的PET瓶都是1pkg,不因体积、面积的不同而改变。
3.2 pkg单位的使用原因
顾名思义,进行包装物的透氧性测试就是为了获取真实的包装物整体透氧数据。以前为了获得包装物的透氧数据需要先检测容器片材的氧气透过量,然后按照容器的表面积以及容器各处的厚度来估算容器整体的透气量。可是容器的壁厚很不均匀,外形很不规则致使难以准确测定容器的表面积,而且材料性质在包装物的吹塑、注塑等生产过程中发生了一定的变化,因此容器透气量的估算结果与实际检测结果确实存在一定的差距,这样直接检测包装物的透氧性就更加重要了。无论包装物的外形如何、厚度是否均匀,都可以利用 pkg单 位表示出包装物整体的氧气阻隔性能,这对进行包装物整体的阻隔性能分析是十分有利的。
4、设备的标定
The oxygen sensor used in this method is a coulometric device that yields a linear output as predicted by Faraday's Law…Experience has shown, however, that under some circumstances the sensor may become depleted or damaged to the extent that efficiency and response are impaired.(这种测试方法中所使用的氧气传感器是一种按照法拉第定律产生线性输出的库仑装置。……经验表明,在一些情况下会出现由于传感器损耗、损坏达到一定程度而削弱传感器的响应效率。)因此,测试系统需要周期标定。标定过程与试验过程相同,标定数据用来计算校正因子Q。Q将直接参与正式试验的结果计算,因此标定系数Q的准确与否直接影响到今后测试结果的准确性。
5、试验过程
5.1 包装物装夹
The method by which a package is prepared for attachment to the instrument for testing depends upon the package shape, type, and test objectives. For a majority of tests, the package may be exposed to ambient air ( 20.8% O2 ). If the package is an extremely good barrier, however, it may be helpful to increase the test gradient by immersing the package in 100% oxygen. This is accomplished by securing a plastic bag or other container around the package and flooding the bag with oxygen.(将包装物装夹到设备上的方法取决于包装物的外形、类型以及测试对象。对于多数试验,包装物可以暴露在环境大气中(20.8%氧气)。但是如果包装物的阻隔性很好,可以把包装物浸入100%的氧气环境中来增加测试浓度梯度,这对试验更加有利。这可以通过用一个塑料袋或是其它容器罩在包装物外面并向其中注入氧气来实现。)图1是标准中给出的包装物装夹示意图,需要注意在容器封口处、以及各进气管、出气管的密封处理。

图 1. 塑料瓶、桶的典型固定方式
Labthink TOY-C1容器/薄膜透氧仪提供了一种方法来实现100%氧气浓度的测试环境(图2),操作简单,重复使用性好。这种装夹结构的最大优点是利用特殊设计轻松实现了包装物两侧的气流循环,而且无需管路支持循环,管路的接头少了,也就减少了设备出现泄漏的可能性。相对于标准中给出的胶封结构(参见图1),它不需要对进气管和出气管进行胶封,因此简化了整套包装物装夹附件的安装和拆卸。
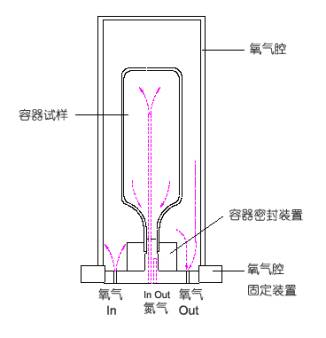
图 2. TOY-C1包装容器固定方式示意图
5.2 测试过程
Preparation of apparatus… The system can then be dried by slowly purging overnight using dry carrier gas ( sensor bypass )… Attachment of the package… Purging the system. Start the nitrogen gas flow and purge air from the package using a flow rate of 50 to 60 mL/min. Maintain this rate for a period determined by the volume of the package… Reduce the rate to a value between 5 and 15 mL/min. Maintain this rate for the next 30 min ( sensor bypassed )… Divert the flow of nitrogen carrier gas to the sensor… When consecutive sensor readings begin to yield the same value, the operator should record this value and label it E e ( package )… Put the sensor in bypass once again. Remove the package from the package fittings and install a stainless steel “perfect package” loop between the carrier gas fittings. After 10 to 15min, divert the flow of carrier gas to the sensor. Maintain this configuration for 30min, or until the sensor output current has descended to a constant low value. Note this value and record as E o ( package )… Place the instrument in a standby condition.(准备设备…然后整夜用干燥载气流缓慢干燥系统(绕开传感器)。…完成包装物附加装置的装夹。…吹洗整个系统。开启50~60mL/min的氮气流净化包装物内的空气,净化时间取决于包装物的体积。…降低氮气流速至5~15mL/min并保持30min(绕开传感器)。…将氮气流引入传感器。…当传感器的连续输出值开始稳定不变时,操作者就可以记下这个值了,这个值就是E e(包装物)。…再次绕开传感器。移走包装物,并在载气装置间插入一个不锈钢材质的“高阻隔包装物”回路。10~15min后,再将载气流引入传感器。保持这种配置30min,或是当传感器的输出电流减小并稳定在一个较低的值上后,就可以把这个值作为Eo(包装物)记录下来。…将设备置于备用状态。)在整个试验过程中,载气流的流速是否合适是至关重要的,必须按照标准精确调节。
5.3 其它注意事项
首先,采用的氧气传感器是消耗型传感器,当传感器的输出信号出现了明显的衰减且无法通过标定系统来弥补时就需要更换传感器。Back diffusion of air into the unit is undesirable.(最好不要出现空气反向渗透进入系统的情况。)这是因为空气中约21%的氧气浓度会使传感器损耗较大,因此在不使用传感器时最好在其内部始终保持有一低流速的氮气流。
其次,进行低阻隔性包装物的检测时可适当降低混合测试气体中的氧气含量。High oxygen concentrations in the carrier gas, as encountered when testing poor barriers, will tend to produce detector saturation. One way to avoid this problem is to immerse the package in a test-gas mixture that provides a lower concentration of oxygen than is found in air. Any subsequent data conversions will require that the O2 partial pressure of such a test gas be known.(当测试阻隔性差的包装物时,载气流中的氧气含量就会很高,这容易引起传感器的饱和。解决这个问题的一条有效途径是将包装物放置在一种混合测试气体中,其中的氧气浓度比空气中的氧气浓度都要低。可以利用测试气体中的氧气分压值进行之后的测试结果换算。)这需要在包装物外面加套塑料袋来保证袋内的氧含量,而且塑料袋的阻隔性要很好,否则由于塑料袋两侧(一侧为空气,另一侧为混合气体)存在氧气浓度差,也会增加袋内的氧气含量,这对于控制测试气体中的氧气含量是不利的,更不利于得出客观准确的试验结果。
再次,需要控制环境温度。The oxygen transmission rate of most plastic materials will vary 3 to 9%/℃. Since the package test attachment does not provide means for control of package temperature, it will prove advantageous from the standpoint of data reproducibility to locate the instrument in a draft-free, constant-temperature environment.(多数塑料的氧气透过率每摄氏度能变化3~9%。由于包装物测试附加装置并没有提供控温功能,因此从试验数据上来看把设备放在没有温漂的恒温环境中更有利于数据的再现性。)
6、总结
ASTM F 1307是目前用于检测包装物透氧性的标准方法。它采用传感器法测试原理;测试结果以包装物为单位,方便对包装物进行整体评价;Reference Package(参考包装物)标定系统得校正因子Q,是测试的重要步骤之一;试样装夹过程繁杂,但是装夹的效果却直接影响到试验结果, Labthink TOY-C1提供的试样装夹方式是解决这个问题的有效方法之一。


 济南兰光新闻中心包含公司动态、公告、产品新闻等多种模块,为您展示最新、最全的企业资讯,让您了解更多包装检测行业的最新技术。
济南兰光新闻中心包含公司动态、公告、产品新闻等多种模块,为您展示最新、最全的企业资讯,让您了解更多包装检测行业的最新技术。 Labthink兰光拥有完善的服务体系,百余人的专业服务团队,能以多种语言通过电话、网络、移动平台、现场等多种途径为全球用户提供真诚、专业、及时、持续的服务和技术支持。
Labthink兰光拥有完善的服务体系,百余人的专业服务团队,能以多种语言通过电话、网络、移动平台、现场等多种途径为全球用户提供真诚、专业、及时、持续的服务和技术支持。